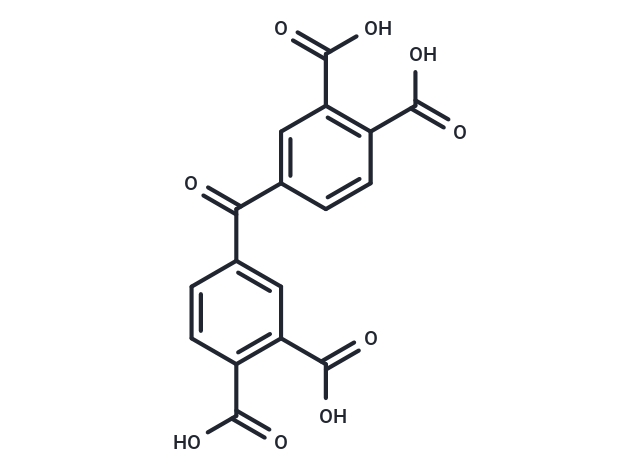
Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid
CAS No. 2479-49-4
Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M33590 CAS No. 2479-49-4
Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid (3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid) is utilized in the preparation of high-performance polyimides and serves as a curing agent for epoxy resins.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 28 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 40 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 53 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 79 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 199 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBenzophenonetetracarboxylic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBenzophenonetetracarboxylic acid (3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid) is utilized in the preparation of high-performance polyimides and serves as a curing agent for epoxy resins.
-
DescriptionBenzophenonetetracarboxylic acid (3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid) is particularly useful in the preparation of high performance polyimides and also useful as curing agents for epoxy resins.
-
In VitroThe kinetics of the photooxidation of aromatic amino acids histidine (His), tyrosine (Tyr), and tryptophan (Trp) by Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid has been investigated in aqueous solutions using time-resolved laser flash photolysis and time-resolved chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization. The pH dependence of quenching rate constants is measured within a large pH range. The chemical reactivities of free His, Trp, and Tyr and of their acetylated derivatives, N-AcHis, N-AcTyr, and N-AcTrp, toward Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid triplets are compared to reveal the influence of amino group charge on the oxidation of aromatic amino acids. Thus, it has been established that the presence of charged amino group changes oxidation rates by a significant factor; i.e., His with a positively charged amino group quenches the Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid triplets 5 times more effectively than N-AcHis and His with a neutral amino group. The efficiency of quenching reaction between the Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid triplets and Tyr and Trp with a positively charged amino group is about 3 times as high as that of both Tyr and Trp with a neutral amino group, N-AcTyr and N-AcTrp.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2479-49-4
-
Formula Weight358.26
-
Molecular FormulaC17H10O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (139.56 mM; Ultrasonic )H2O : 10 mg/mL (27.91 mM; Ultrasonic)
-
SMILESC(=O)(C1=CC(C(O)=O)=C(C(O)=O)C=C1)C2=CC(C(O)=O)=C(C(O)=O)C=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Mengxian Ding, et al. Process for the preparation of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic acid and its derivatives. Jan. 14, 1992. US5081281A.
molnova catalog



related products
-
RP 48497
RP 48497 is a photodegradation product of Eszopiclone. Eszopiclone is used in the treatment of insomnia.
-
JG-2016
JG-2016, as a small molecule histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1) inhibitor, inhibits the growth of human cancer cell lines, inhibits enzyme activity in cellulose, and interferes with tumor growth.
-
Glaucoside C
Glaucoside C is a natural product for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


